Understanding the Cervical Splenius Muscle: Anatomy, Function, and Common Issues
The cervical splenius muscle is a small yet vital muscle located in the neck region. Despite its relatively small size, this muscle plays a significant role in our daily activities, from turning our heads to maintaining proper posture. In this article, we will take a closer look at the anatomy, function, and common issues associated with the cervical splenius muscle. We will explore how this muscle works in conjunction with other muscles in the neck and upper back, and how it can contribute to a variety of conditions, including headaches, neck pain, and fatigue. Whether you’re a fitness enthusiast, office worker, or simply someone interested in learning more about the human body, this article is a valuable resource for understanding the importance of the cervical splenius muscle and how to keep it healthy and functioning properly. So, let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of the cervical splenius muscle!
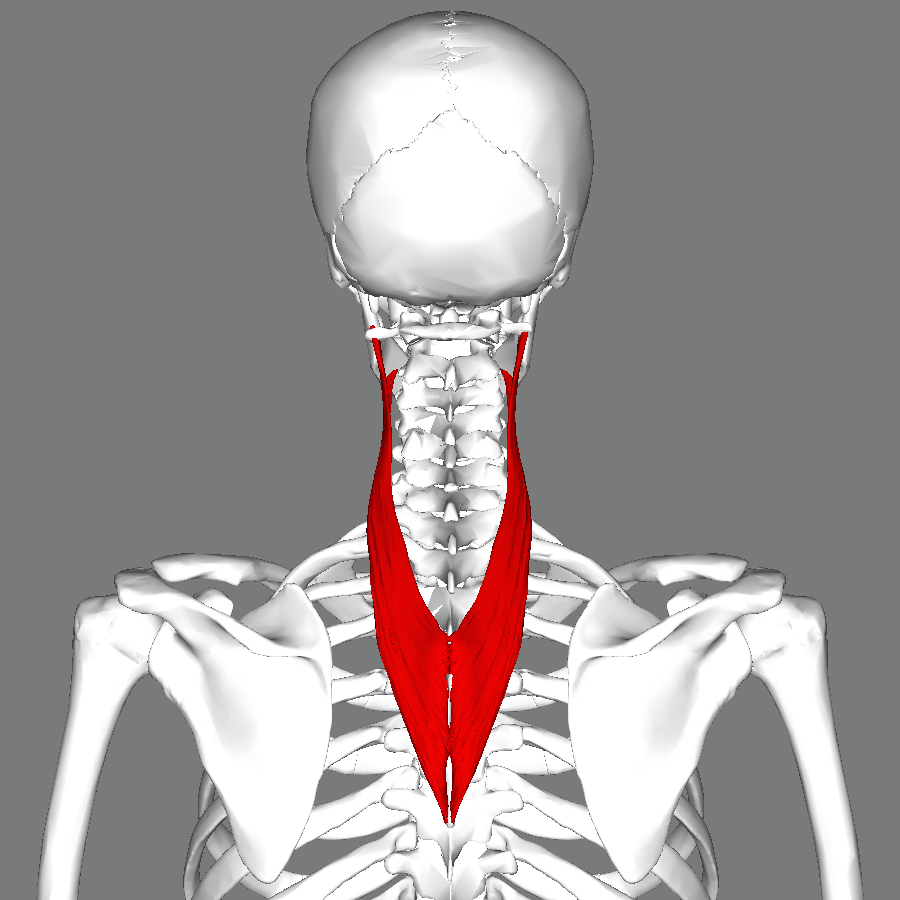
Anatomy of the cervical splenius muscle
The cervical splenius muscle is a narrow, flat muscle that extends from the upper thoracic vertebrae to the base of the skull, and is located in the back of the neck. It is divided into two parts – the splenius capitis and the splenius cervicis. The splenius capitis is located at the back of the head, while the splenius cervicis is located in the upper cervical region. These two parts work together to help us rotate and extend our heads.
The cervical splenius muscle is innervated by the dorsal rami of the spinal nerves, and receives its blood supply from the deep cervical artery. The muscle is surrounded by several other muscles, including the trapezius, levator scapulae, and rhomboids, which work together to support the head and neck.
Functions of the cervical splenius muscle
The cervical splenius muscle has several important functions, including head rotation, neck extension, and lateral flexion. These movements are essential for our daily activities, from driving and reading to playing sports and exercising. The muscle also helps to maintain proper posture, by supporting the weight of the head and neck and preventing slouching or hunching over.
In addition to its physical functions, the cervical splenius muscle is also connected to our emotional and mental well-being. Tension or pain in this muscle can be caused by stress or anxiety, and can contribute to headaches, fatigue, and other physical and emotional symptoms.
Common issues associated with the cervical splenius muscle
The cervical splenius muscle is prone to a variety of issues, including tension, pain, and inflammation. These issues can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor posture, stress, injury, or underlying medical conditions.
One common issue associated with the cervical splenius muscle is tension headaches. Tension headaches are caused by muscle tension or spasms in the neck and head region, and can be triggered by stress, anxiety, or poor posture. The cervical splenius muscle is often involved in tension headaches, as it can become tight or strained from prolonged periods of sitting or standing, or from repetitive motions such as typing or driving.
Another common issue associated with the cervical splenius muscle is neck pain. Neck pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor posture, injury, or underlying medical conditions. The cervical splenius muscle is often involved in neck pain, as it can become strained or inflamed from overuse or injury.
Causes of cervical splenius muscle pain
Cervical splenius muscle pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor posture, stress, injury, or underlying medical conditions. Poor posture, such as slouching or hunching over, can put undue stress on the cervical splenius muscle and cause it to become tight or strained. Stress and anxiety can also contribute to tension in the neck and shoulder region, which can affect the cervical splenius muscle.
Injury, such as whiplash or a sports injury, can also cause cervical splenius muscle pain. In these cases, the muscle may become strained or inflamed, and may require rest, ice, and other treatments to heal properly. Underlying medical conditions, such as arthritis or fibromyalgia, can also contribute to cervical splenius muscle pain, and may require medical intervention to manage.
Symptoms of cervical splenius muscle pain
Cervical splenius muscle pain can manifest in a variety of ways, including headaches, neck pain, shoulder pain, and fatigue. Tension headaches are a common symptom of cervical splenius muscle pain, and may be felt as a dull ache or pressure in the temples or forehead. Neck pain may be felt as a sharp or dull ache in the neck region, and may be accompanied by stiffness or limited range of motion. Shoulder pain may also be present, as the cervical splenius muscle is connected to the shoulder region and can contribute to pain and tension in this area. Fatigue may be felt as a general sense of tiredness or exhaustion, and may be caused by the physical and emotional strain of cervical splenius muscle pain.
Diagnosing cervical splenius muscle pain
Diagnosing cervical splenius muscle pain can be challenging, as it may be caused by a variety of factors and may present with a range of symptoms. A thorough physical examination, including a review of medical history and a neurological exam, may be necessary to identify the underlying cause of cervical splenius muscle pain. Imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI scans, may also be used to rule out any underlying medical conditions or injuries.
Treating cervical splenius muscle pain
Treating cervical splenius muscle pain depends on the underlying cause of the pain. In cases where poor posture or stress is the cause of the pain, lifestyle changes such as improving posture, reducing stress, and incorporating regular exercise and stretching may be recommended. In cases where injury or underlying medical conditions are the cause of the pain, medical intervention such as physical therapy, medication, or surgery may be necessary.
Massage therapy and other manual therapies may also be beneficial in relieving cervical splenius muscle pain. These therapies can help to reduce muscle tension and inflammation, and may promote relaxation and stress relief.
Exercises to strengthen the cervical splenius muscle
Incorporating exercises to strengthen the cervical splenius muscle can help to improve posture, reduce pain, and prevent further injury. Some exercises that may be helpful include neck rotations, head tilts, and shoulder shrugs. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or certified personal trainer before starting any new exercise program, to ensure that you are performing the exercises correctly and safely.
Prevention of cervical splenius muscle pain
Preventing cervical splenius muscle pain involves maintaining good posture, reducing stress, and incorporating regular exercise and stretching. It is important to take frequent breaks when sitting or standing for long periods of time, and to avoid repetitive motions such as typing or driving. Regular exercise and stretching can help to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension, which can prevent further injury and pain.
Conclusion
The cervical splenius muscle is a small yet important muscle in the neck region that is responsible for a variety of movements and functions. Understanding more about the anatomy, function, and common issues associated with this muscle can help us maintain better posture, reduce pain, and improve our overall physical and emotional well-being. If you are experiencing cervical splenius muscle pain or other symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How does the splenius cervicis muscle contribute to neck movement?
The splenius cervicis muscle supports the neck, enabling flexion and lateral movements [6].
Q2: What is the origin and insertion of the splenius cervicis muscle?
The splenius cervicis muscle originates from the spinous processes of the third to the sixth thoracic vertebrae and inserts into the posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the upper two or three cervical vertebrae [1].